ANNUAL STEERING GROUP MEETING FOR ONSSET AND ONSTOVE MODELLING TOOLS
The Annual Steering Group Meeting for the OnSSET open-source modelling tool for electrification planning took place at ICTP Trieste on Friday, 16 August 2024. The meeting was co-chaired by SEforALL and The World Bank.
Attending institutions were CCG, Sustainable Energy for All, UK Aid, MECS Modern Energy Cooking Services, and several universities including KTH Royal Institute of Technology (Sweden), University of Cape Town (South Africa), University of Oxford (UK), and Strathmore university (Kenya).
CCG has now established a new Model Curator role for OnSSET and OnSTOVE, which will oversee and manage the ongoing maintenance, improvement, and development of these tools to ensure they remain up-to-date and functional in the long term.
Members shared many exciting innovations regarding the ways in which the OnSSET tool is being improved and applied to address important policy issues relating to universal access to energy.
- The World Bank highlighted the launch of the Global Electrification Platform 3.0, which improves integration with system planning and incorporates carbon pricing considerations.
- In Kenya, the application of a new geospatial tool that enhances building recognition is allowing for more sophisticated estimation of non-residential demand.
- In Sierra Leone, soft linking of OnSSET with the energy system capacity expansion modelling tool OSeMOSYS is allowing iterative joint optimization of electrification and system expansion.
- Methodological improvements include the OMG tool (Open-Source Spatial Electrification Toolkit for Mini Grids) that allows OnSSET to zoom into the more detailed design of specific mini-grid projects, as well as enhanced algorithms for generating population clusters and designing grid architecture.
- An ambitious list of potential innovations to the tool were shared and discussed, such as prioritization based on net benefits, connecting investment to financing options, and incorporation of affordability considerations. Other potential innovations include integration of supply reliability measures, improvement of load curves and temporal granularity of solutions, and enhancement of transmission and distribution network modelling. Implementation of model improvements will need to be done in combination with upgraded management, versioning and documentation of the tool.
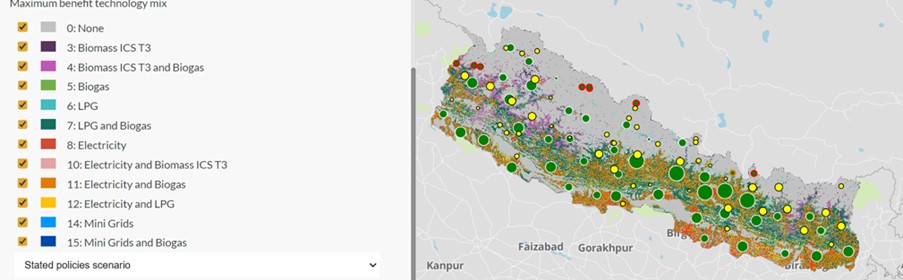
Notably, this gathering also served as the first Annual Steering Group Meeting for the OnStove open-source modelling tool that supports the achievement of clean cooking goals. OnSSET and OnStove are companion tools, each based on a similar geospatial optimisation paradigm, and both supporting the achievement of SDG 7.1 on achievement of universal access to sustainable energy.
Discussions of OnSTOVE were chaired by KTH, with support from SEforALL and the World Resources Institute (WRI). MECS, the World Bank, Duke University (United States) and Strathmore University (Kenya) all took part.
Early applications of OnStove were shown to be extremely promising, demonstrating the huge social benefits associated with the adoption of clean cooking. They also highlighted significant positive synergies between clean cooking and electrification, since wider adoption of electricity for cooking (as this becomes increasingly viable), greatly improves the economic case for electricity by boosting demand.
By way of further enhancements, the OnStove Steering Group plans more user-friendly interfaces and improved training materials. Proposed technical innovations include the incorporation of fuel stacking, a better representation of fuel supply chains, and the integration of affordability considerations.